Page Contents :
Why Is Delegated Proof Of Stake
In the previous post, we learned about Proof of Work (PoW) ![]() and Proof of Stake (PoS)
and Proof of Stake (PoS) ![]() and discussed how consensus mechanisms work.
and discussed how consensus mechanisms work.
PoW offers robust security but comes at the cost of high energy consumption.
PoS, on the other hand, eliminates the need for external resources, and its consensus mechanism is considered more efficient.
Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) is a variant of PoS and takes the PoS mechanism to the next level.
DPoS was first proposed by Daniel Larimer in 2014.
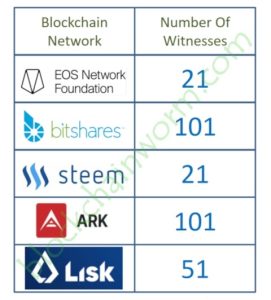
It is a blockchain consensus algorithm used by several cryptocurrency projects, including Bitshares, Steem, Ark, and Lisk.
The DPoS consensus algorithm works through a voting system with two roles – notaries and witnesses.
Notaries refer to equity holders who can vote to elect block producers.
While witnesses refer to selected nodes to produce and verify new blocks.
In other words, DPoS operates like a “People’s Congress,” where the community elects a few representatives to vote and keep records.
The voting power is proportional to the number of coins held by each user, and the voting system varies from project to project.
Compared to the previous PoS mechanism, the DPoS consensus algorithm is seen as a more effective and democratic version.
The DPoS algorithm aims to simplify the block generation process.
Unlike competition-based PoW systems, the actual block generation process is competition based.
DPoS has a predetermined block generation process.
Each witness takes turns producing blocks.
As a result, it is more scalable and can handle a higher number of transactions per second (TPS).
Understanding The Key Differences Between DPoS & PoS
PoS and DPOS are two widely used consensus mechanisms in blockchain networks.
Both of them use to validate transactions and secure the network.
The main difference between PoS and DPoS lies the number of validators involved in the processes.
In PoS, any user holding a certain amount of coins can participate in validating transactions and adding blocks to the chain.
However, this approach can lead to centralization issues as users with more coins have more voting power and influence over the network.
DPoS addresses these drawbacks by reducing the number of validators to a smaller group of elected representatives called witnesses.
EOS, for instance, currently has over 200,000 addresses holding tokens and can vote for up to 30 block producers.
The witnesses are responsible for achieving consensus in the process of producing and verifying new blocks.
DPoS limits the importance of equity in the process of electing block producers.
Therefore this system can process a large number of on-chain transactions quickly.
It is more efficient than PoS, which can be slower due to more validators involved.
As a result, it is an even more attractive option for those concerned about energy consumption and environmental impact.
And a more sustainable and efficient consensus mechanism for securing blockchain networks.
How Delegated Proof Of Stake Works
DPoS operates differently from the traditional PoW and PoS mechanisms.
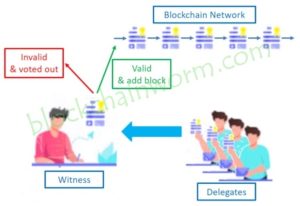
- Stakeholders who hold a certain amount of coins in a DPoS network are eligible to elect witnesses to validate transactions and produce new blocks.
- These witnesses, also known as delegates or block producers, take turns in creating blocks.
- Block producers are responsible for verifying transactions and appending them to the blockchain, similar to the mining process in PoW.
However, this process does not require the same level of computational power. - Witnesses use a process called validation and consensus to verify transactions and create new blocks.
- During validation and consensus, witnesses check the validity of transactions and agree on the order in which they should be added to the blockchain.
- The election of witnesses is done by the stakeholders and they need to maintain a good reputation to stay in their position.
- If a witness fails to fulfill their responsibilities or behaves improperly, they can be voted out of their position by the stakeholders.
- Witnesses receive rewards in the form of transaction fees and newly created coins through block production.
- They can distribute these rewards to the stakeholders who voted for them to incentivize continued support.
Why The Witness Mechanism Could Solve Centralization Issues
In this section, we will discuss how the witness mechanism in the DPoS algorithm can help ensure the decentralization of the network.
As mentioned earlier, witnesses are responsible for verifying transactions and adding them to the blockchain in a DPoS network.
Unlike PoS, where any user holding a certain amount of coins can participate in the process of validating transactions.
DPoS limits the number of validators to a smaller group of elected representatives.
This approach reduces the potential for centralization because in PoS, users with more coins have more voting power and influence over the network.
This can lead to centralization issues, as users with more coins can dominate the process of validating transactions.
In DPoS, witnesses need to maintain a good reputation to stay in their position.
This helps to ensure that only the most trustworthy and competent witnesses are elected to produce and validate blocks.
Moreover, witnesses receive rewards and distribute them to the stakeholders who voted for them as a way of incentivizing the stakeholders to continue supporting them.
This further strengthens the decentralization of the network and ensures that power is distributed among a large number of stakeholders.
Therefore, the witness mechanism plays a vital role in DPoS, ensuring that the network remains decentralized and secure.
Why Scalability Is A Crucial Factor For Blockchain
Scalability is a crucial factor for any blockchain technology, as it determines the network’s ability to handle a growing number of transactions.
In this regard, DPoS has emerged as one of the most scalable consensus algorithms in the blockchain ecosystem.
Let’s dive deeper into why scalability is so important for DPoS!
One of the significant advantages of DPoS over other consensus algorithms is its ability to scale efficiently.
With DPoS, block producers are chosen based on their performance and reputation in the network, and they take turns producing blocks.
As a result, DPoS can handle a significantly higher number of transactions compared to PoS and PoW.
Scalability is essential for DPoS because it enables the network to process more transactions per second, making it more attractive to users and enterprises.
As more users adopt blockchain technology, the number of transactions on the network will increase, and the need for scalability will become even more crucial.
Scalability is also crucial for the adoption of DPoS by businesses and organizations.
Businesses need to process a large number of transactions efficiently to ensure their operations run smoothly.
In this regard, DPoS is more attractive than PoW or PoS because it can handle a higher number of transactions in a shorter amount of time.
This makes DPoS more suitable for enterprise-level applications.
Furthermore, scalability is also essential for the long-term sustainability of DPoS.
As the number of users and transactions on the network grows, the network needs to scale to maintain its efficiency and reliability.
Without scalability, the network may become congested, leading to longer transaction times and higher fees.
This can lead to a decline in user adoption and ultimately, the network’s failure.
In summary, the scalability of DPoS is critical for its adoption, sustainability, and long-term success.
With its ability to handle a high volume of transactions, DPoS offers an attractive solution to businesses and users seeking a more scalable blockchain technology.
As the blockchain ecosystem continues to grow, scalability will remain a crucial factor for the adoption and success of DPoS.
Advantages & Disadvantages Of DPoS
In this section, we will explore some of the pros and cons of DPoS.
High transaction throughput:
DPoS can process a large number of transactions quickly and efficiently compared to other consensus mechanisms.
This is due to the smaller number of validators involved, which makes the process faster and more streamlined.
Energy-efficient:
DPoS requires less computational power than other consensus mechanisms like PoW, which makes it more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Reduced centralization:
By limiting the number of validators to a smaller group of elected representatives, DPoS reduces the potential for centralization.
This helps to prevent users with more coins from dominating the process of validating transactions.
Decentralized governance:
DPoS provides a mechanism for stakeholders to participate in the governance of the network.
This ensures that decision-making power is distributed among a large number of stakeholders, rather than being controlled by a small group of individuals.
Risk of voter apathy:
In DPoS, voters are responsible for electing witnesses to validate transactions. However, voter apathy can result in a small group of stakeholders controlling the election process, which can lead to centralization.
Risk of collusion:
If a small group of stakeholders colludes to elect witnesses, they can control the validation process and potentially manipulate the network.
Cost of running a node:
Running a node in a DPoS network can be costly, as it requires a certain amount of coins to participate in the election process.
This can make it difficult for small stakeholders to participate in the network.
The Future Of DPoS
The future development of DPoS is promising, as it continues to gain popularity due to its scalability and efficient consensus mechanism.
Some potential developments include improving the voting system to increase participation, enhancing security features to prevent malicious attacks, and exploring interoperability with other blockchain platforms.
Additionally, as the demand for decentralized finance (DeFi) ![]() and non-fungible tokens (NFTs)
and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) ![]() increases, DPoS may play a significant role in facilitating these transactions due to its ability to handle high transaction volumes.
increases, DPoS may play a significant role in facilitating these transactions due to its ability to handle high transaction volumes.




